How to Calculate Cutting Length of Stirrups in columns
Cuttting Length of Rectangular and circular Stirrups

How to Calculate Cutting Length of Stirrups in columns
What Is Stirrup?
A stirrup is a closed loop of rebars in a reinforced concrete component that holds the main reinforcement (RFT) bars together. Depending on the design and shape of the structural members, stirrups may be of various types.
Stirrups are made of steel rebars that are wrapped around the top and bottom bars of rectangular or circular beams or columns.
Spiralen sind normalerweise parallel zur Längsrichtung des RFT positioniert, aber sie können auch diagonal positioniert sein.
In order to avoid shear failure, which occurs in beam cracks and is typically diagonal, it is done. Es ist am besten, dass der Designer die Stirnraddistanz entlang der Welle angegeben hat.
Various types of stirrups used in building
There are different kinds of stirrups for different situations.
Types Of Stirrup Based On Shape:
- Rectangluar Stirrup
- Square Stirrup
- Circular or Round Stirrup
- Triangular Stirrup
- Stirrups On a Spiral
Read More
-
What is the Bricks & Important Tests on Brick
-
Technology for the locating underground utilities
-
Difference between a one-way slab and a two-way slab
-
Components, Transportation, and Storage of Rainwater Harvesting Methods
-
Types Of Vibrators Used In the Construction
Types Of Stirrup Based On Nature Of Construction
Single-legged Stirrups (Open Stirrup)
Single-legged stirrups aren’t very common, but they can be useful when you only need to tie two rods. These stirrups have only one leg and look like a flattened U instead of a full loop.
Stirrups with two legs or double legs (closed stirrups)
In construction, stirrups with two legs are the most common. To make this kind of stirrup, you need at least four rods.
Four-legged Stirrups (Closed Stirrup)
The four-legged stirrup is the next level up. It has two stirrups that overlap and don’t cover all of the rods. If you have eight rods in two rows of four, the two stirrups will each wrap around six rods. The four rods in the middle will be wrapped by both stirrups.
Six-legged Stirrups (Closed Stirrup)
A stirrup with six legs can be used to hold up the same number of rods as an eight-legged stirrup. In this setup, a single stirrup goes around all eight rods, and extra legs provide extra support. Most of the time, these extra legs go between two nearby rods.
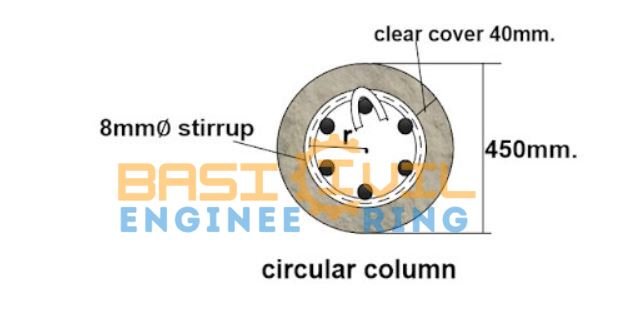
Calculation Cutting Length of Circular Stirrups
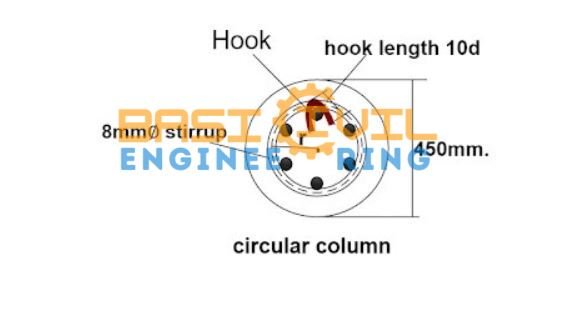
Given Data
Diameter of circular column D = 500mm
Clear cover = 50mm.
The diameter of stirrup d = 12mm.
Farmula of cutting length of the circular stirrup
= [2πr + ( 2nos. × hook length ) – ( 2nos. × hook bend. ) ]
= [ 2πr +( 2nos. × 10d ) – ( 2nos. × 2d )
d = diameter of the stirrup.
r = radius of the centerline of the circular stirrup ( as shown in the drawing).
First, we will calculate the value of r from the given data.
r = [ (1/2 × diameter of column ) – clear cover – ( 1/2 × diameter of stirrup bar )]
r = [ (1/2 × 500mm ) – 50mm – ( 1/2 × 12mm ) ]
r = [ 250mm – 50mm – 6mm ]
r = 194mm.
length of the circular stirrup
= [ ( 2 × π × 194mm ) + ( 2nos × 10d ) – ( 2nos. × 2d ) ]
= [ ( 2 × 3.142 × 194mm ) + ( 2nos. × 10 × 12mm ) – ( 2nos. × 2 × 12mm. )]
= [ 1280.32 mm + 240mm – 48mm ]
= 1472.32mm
= 1.473m.
Calculate Cutting Length of Rectangular Stirrups
Rectangular Column
Most of the time, they are used in building construction. In practise, these types of columns are only used in rooms that are square or rectangular. It is much easier to build and cast square or rectangular columns than it is to make round ones.
site Of Column = 500mm x 400mm
Length Of Column (A) = 500 – (2 x 44) = 412mm
Breadth Of Column (B) = 400 – (2 x 44) = 312mm
Hook Length = 10 D = 10 x 8 = 80 x 2 = 160mm
Cutting Length Of Stirrup = (A x2) + (B x2) + Hook Length
= (412 x2) + (312 x2) + 160
Cutting Length Of Stirrup = 1608 mm / 1000 = 1.608m
Purpose of Stirrups in Reinforcement
To get the right amount of stress resistance, we have to put the right number of bars in the right places. We’ve already talked about how a load affects a column in Types of Column Failure, where we talked about compressive and buckling stress.
Each load that acts on a column causes some kind of movement, cracking, or tension in the reinforcement. So the main purpose of stirrups is
- To hold the support in place
- To stand up to the bending and shearing stress that built up in the reinforcement.
- To stop diagonal tension cracks from spreading, even though they are small,
- It makes the column stronger against pressure.
- It can make the column more flexible.
- Stirrups make sure that the main reinforcement in a column doesn’t buckle.
- During the concrete process, it keeps the main reinforcement from moving.
- Change the way the dowels reinforce the column.
- Stirrups are used in the same way in a beam as they are in a column.
- To provide lateral confinement to longitudinal bars
- It protects against shear and twisting forces.
- To keep long bars in place while building
- It keeps the concrete in the centre, which makes it stronger and more flexible.
- It keeps individual bars from buckling too soon.